Consider the following real-life scenarios:
- An airline’s AI-powered chatbot promises a customer that it could provide a steep discount for a bereavement flight – a promise that goes directly against company policy. A court later ruled that the airline had to honor the promise.
- A researcher gathering background information on a prominent professor discovers evidence that the professor had been accused of making sexually suggestive comments and attempting to inappropriately touch a student – but it turns out that ChatGPT invented both the story and the citations to it.
- HR uses AI to develop a job description for an entry-level role but didn’t read it closely enough before posting it. After no one applied, the HR reps discover that the opening required candidates to have five to seven years of experience.
- The Chicago Sun-Times and Philadelphia Inquirer (and others) publish a syndicated summer reading list to guide readers about the next great book they should pick up for vacation – but it turns out that 10 of the 15 recommended books were made up out of thin air by GenAI.
(To prove to you these stories are all very real, you can find details about them here, here, here, and here.)
These are all examples of AI “hallucinations” – situations where generative AI produces incorrect or blatantly false pieces of information that sound all too real. And each of them caused some sort of damage to the businesses involved. What’s going on when you get one of these results, and what are some steps you can take so your business isn’t the latest to fall victim to this very concerning trend?
|
🏊 Dive Deeper! Join our next interactive AI Forum to discuss hallucinations with FP’s Director of AI (Pritesh Patel), Co-Chair of AI Practice Group (Dave Walton), and Chief Content Officer (Rich Meneghello). Register for this free July 30 event here! |
What Are AI Hallucinations – and Why Should You Care?
AI hallucinations are confidently incorrect outputs generated by large language models (LLMs). They happen because GenAI is designed to predict the most likely next word, not to verify facts. Remember, “artificial” intelligence simulates knowledge but doesn’t embody it. And when GenAI fills in the blanks with fiction, it does so with the tone and confidence of truth – which is what makes hallucinations so dangerous.
4 Biggest Reasons Hallucinations Occur
AI hallucinations usually stem from a combination of design limitations, user error, and model architecture.
- Predictive Generation Without Grounded Facts – As PwC and Forbes note, LLMs aren’t connected to live data unless explicitly integrated. They don’t “know” truth – they just produce what sounds plausible. When asked about unfamiliar or nuanced topics, they may fabricate content in a confident tone.
- Poor Prompts or Ambiguous Requests – According to phData, vague, imprecise, or overly broad prompts increase hallucination risk. If you ask for technical, legal, or factual summaries without giving grounding material, the model may make up references or assumptions.
- Overuse of "Expert Voice" Prompts – SeniorExecutive.com highlights that asking GenAI to write “as a lawyer” or “as a policy expert” often results in made-up language that sounds more authoritative and is more likely to be trusted, even when the facts are fabricated.
- Model Limitations and Data Gaps – IBM and CapTechU explain that hallucinations are more common when the model compresses complex content into short outputs, data is outdated or biased, the user asks about post-training events; and context is too limited to support the task.
Business Risks Caused by AI Hallucinations
Hallucinations are a cross-functional risk that can impact just about every aspect of your business. Here are just eight ways they can impact your organization:
- Reputational Damage – Publishing or promoting false content undermines your credibility.
- HR Missteps – Misleading job postings or benefits summaries can cause compliance failures.
- Customer Service Failures – Chatbots making unauthorized promises can bind you to false terms.
- Operational Disruption – Acting on flawed summaries or recommendations wastes resources.
- Security/Privacy Breaches – AI may hallucinate real-sounding but inaccurate personal or confidential information.
- Legal Liability – Fake citations, inaccurate policies, or misapplied legal analysis can result in sanctions or lawsuits. (Check out this up-to-date list of published legal decisions where GenAI produced hallucinated content – over 220 such incidents and counting!)
- Audit and Compliance Failures – Hallucinated outputs may slip into public-facing disclosures or regulatory filings.
- Financial Loss – Misguided investment decisions based on fabricated forecasts or pricing data.
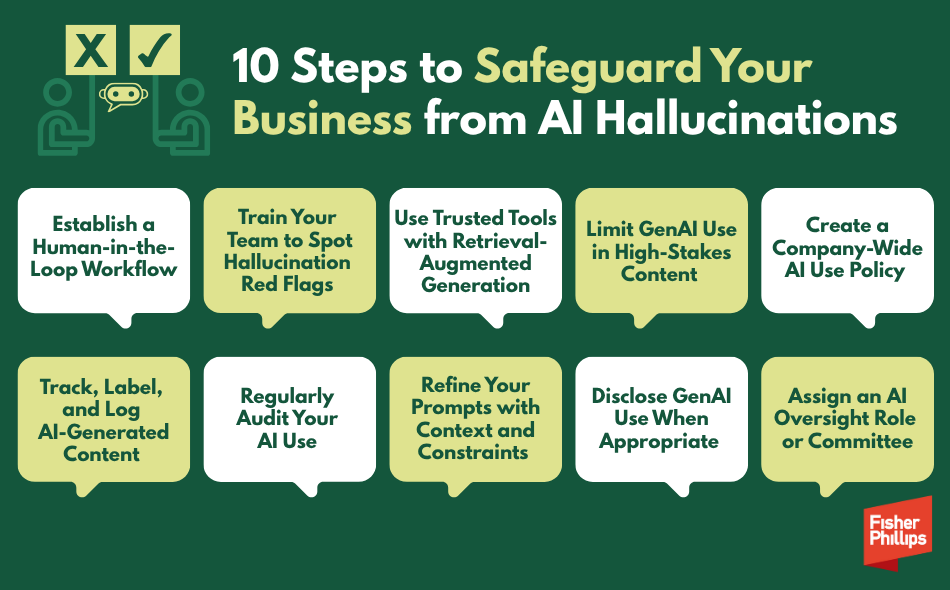
10 Steps to Safeguard Your Business from AI Hallucinations
The following actions can help your business reap GenAI’s benefits while avoiding hallucinatory pitfalls:
1. Establish a Human-in-the-Loop Workflow – Never publish or act on GenAI content without human review – especially in legal, HR, or compliance contexts.
2. Train Your Team to Spot Hallucination Red Flags – They include overconfident tone, fake citations, and lack of links. Train employees to verify outputs and ask: whether they can independently confirm the data.
3. Use Trusted Enterprise Tools with Retrieval-Augmented Generation – Some models integrate with real-time data sources, reducing risk. Look for vendors with citations and source linking, knowledge base integrations, and built-in risk warnings.
4. Limit GenAI Use in High-Stakes Content – GenAI works best as a first draft, not a final authority. And it’s especially important to avoid GenAI-generated content in:
- Contracts
- Regulatory filings
- Public statements
- Policy documents
5. Create a Company-Wide AI Use Policy – If you ask your workers to use GenAI, make sure you create a policy that outlines who can use GenAI and when, what types of prompts are allowed, what outputs require approval, and when to disclose AI involvement externally.
6. Track, Label, and Log AI-Generated Content – You may want to consider treating GenAI output like any other data source. In such cases, you’ll want to document the prompt, who created it, how it was reviewed, and where it was published.
7. Regularly Audit Your AI Use – Conduct quarterly or semi-annual audits to identify rogue AI usage (e.g., unapproved tools), review content that was published with GenAI assistance, and update training materials with real-world examples.
8. Refine Your Prompts with Context and Constraints – Use templates and structure your queries. Vague prompts like “summarize this document” invite hallucinations. Add grounding such as: “Summarize this document using only the facts below, identify where you found each portion you summarize, and cite the attached links.”
9. Disclose GenAI Use When Appropriate – If customers, clients, or employees are interacting with GenAI, let them know. Transparency builds trust and reduces surprise when errors occur.
10. Assign an AI Oversight Role or Committee – You should consider naming an internal point person or task force responsible for reviewing policies, handling hallucination-related incidents, and staying current on legal developments.
|
💡 Want More? Join our next interactive AI Forum to discuss hallucinations with FP’s Director of AI (Pritesh Patel), Co-Chair of AI Practice Group (Dave Walton), and Chief Content Officer (Rich Meneghello). Register for this free July 30 event here! |
Suggested Further Reading
- How to Detect and Mitigate AI Hallucinations (Shelf.io)
- AI Hallucination Risks and Action Steps (SeniorExecutive.com)
- How Businesses Can Mitigate AI Hallucination Impact (Forbes Tech Council)
- Mitigating and Preventing AI Hallucinations (IBM Think)
- Combatting Falsified Information in GenAI (CapTechU)
Conclusion
We will continue to provide the most up-to-date information on AI-related developments, so make sure you are subscribed to Fisher Phillips’ Insight System. If you have questions, contact your Fisher Phillips attorney, the authors of this Insight, or any attorney in our AI, Data, and Analytics Practice Group.